Introduction
As technology continues to play an integral role in our lives, individuals with disabilities increasingly rely on digital platforms for communication, information, and access to goods and services. With the growing number of individuals with disabilities relying on digital platforms, it is crucial for businesses and organizations to ensure that their websites and applications are accessible to all. One of the most important standards to adhere to is the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
In this guide, we will provide you with an ADA compliance checklist and essential tips to help you create an inclusive digital presence. By following these guidelines, businesses can successfully engage and cater to the expanding population of individuals with disabilities. So, let’s begin!
Evolution of ADA and the Progress of Digital Accessibility
Since its enactment in 1990, the ADA has undergone significant developments to address the challenges faced by disabled individuals in accessing digital content and services. Initially, the ADA primarily focused on physical accessibility, but with the rise of the digital age, it became necessary to extend its scope to digital platforms.
Over time, the understanding of digital accessibility has evolved, recognizing that people with disabilities should have equal access to information, communication, and technology. This has led to the emergence of guidelines and standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which provide a framework for ensuring digital content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users, including those with disabilities.
Relationship Between WCAG and ADA Compliance
WCAG, which stands for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, is closely related to ADA compliance. The ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) is a U.S. federal law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities and requires equal access to goods, services, and information, including those provided through websites and digital platforms.
WCAG is a set of internationally recognized guidelines developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that provides recommendations for making web content more accessible to people with disabilities. It outlines specific techniques and success criteria to ensure websites are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for users with various disabilities.
Although the ADA does not explicitly mention websites or provide specific technical standards, courts have generally interpreted the law to apply to websites as well. As a result, many organizations and businesses in the United States strive to make their websites accessible to comply with the ADA.
To achieve ADA compliance for websites, organizations often turn to the WCAG guidelines as a recognized industry standard. The most widely adopted version of these guidelines is WCAG 2.0, which was published in 2008. However, in 2018, the W3C introduced an updated version called WCAG 2.1 to address additional accessibility requirements.
WCAG 2.1 builds upon the principles and success criteria of WCAG 2.0, but includes new guidelines to enhance accessibility for individuals with cognitive and learning disabilities, as well as for users on mobile devices. Some of the new features in WCAG 2.1 include:
- Improved support for touch-based interactions and mobile accessibility.
- Guidelines to address people with low vision and cognitive disabilities.
- Additional success criteria for making content accessible on a wider range of devices.
Must-Have ADA Compliance Checklist
When it comes to ensuring ADA compliance, there are several key areas that should be addressed to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Here is a checklist of key considerations to help organizations evaluate their compliance with ADA:
Conducting an Accessibility Audit
Start by conducting a thorough accessibility audit of your website or digital platforms. This involves assessing the overall accessibility of your content, including website structure, navigation, multimedia elements, forms, and interactive features. Use automated accessibility testing tools, as well as manual testing by individuals familiar with accessibility guidelines, to identify potential barriers and areas for improvement.
Bank of America
They have prioritized accessibility in its banking services, both online and in physical branches. They offer accessible ATMs, braille and large-print materials, and trained staff to assist customers with disabilities. These efforts have not only made banking more inclusive but have also resulted in positive customer experiences and loyalty among individuals with disabilities.
Making Your Content Accessible
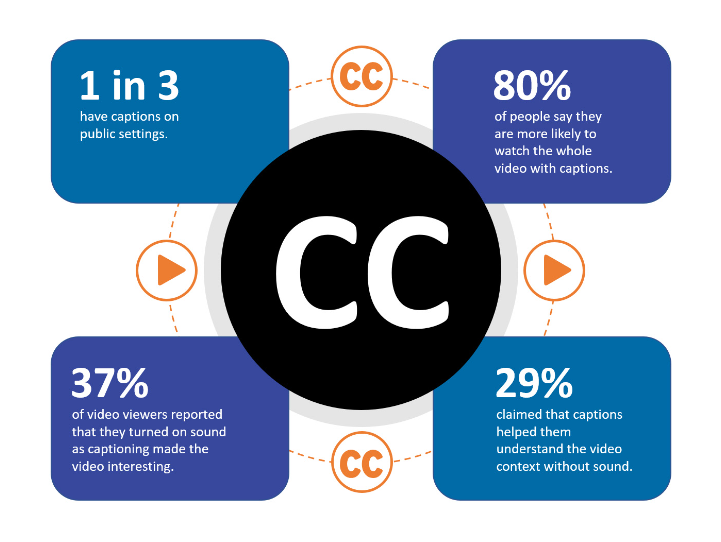
To ensure accessibility, it is crucial to make your content inclusive and easily consumable by all users. This includes providing alternative text for images, captions or transcripts for videos, and descriptive headings for easy navigation. Use clear and concise language in your text content, avoiding jargon or complex sentence structures. Ensure that your website is structured properly using semantic HTML, allowing assistive technologies to interpret the content accurately. Additionally, provide resizable text options and ensure that the site remains functional and usable when text is enlarged.
Netflix
The popular streaming platform provides closed captioning and subtitles for a wide range of their content, making it accessible to deaf and hard-of-hearing viewers. This initiative has not only allowed people with hearing disabilities to enjoy Netflix’s vast library of movies and TV shows but has also attracted a larger audience.
Keyboard Accessibility
Keyboard accessibility is a fundamental requirement for ADA compliance. It means that all functionality and interactive elements on your website should be operable using only a keyboard. This is essential for individuals who rely on assistive technologies like screen readers or alternative input devices. Ensure that users can navigate through your website, interact with buttons, links, dropdown menus, and form fields using keyboard commands.
Apple
Apple has made accessibility a core component of its products, including iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers. They offer features like VoiceOver (screen reader), Switch Control, AssistiveTouch, live captions, and a variety of customization options to accommodate different accessibility needs.
Assistive Technology Compatibility
Consider compatibility with assistive technologies, such as screen readers, screen magnifiers, or voice recognition software. Your website should work seamlessly with these tools to provide equal access to all users. Avoid using technologies that are incompatible with assistive devices, such as Flash, which is not supported by many screen readers.
Microsoft
A technology company has developed features such as built-in screen readers, keyboard shortcuts, and speech recognition software to assist individuals with disabilities in using their software. According to a Microsoft report, implementing accessibility features in their products has expanded their customer base, resulting in an estimated $100 billion in annual revenue.
Ongoing Maintenance and Testing
ADA compliance is an ongoing process, and it is essential to regularly maintain and test your website for accessibility. Conduct regular audits to identify any new accessibility issues that may arise due to content updates or design changes. Test your website on different browsers and devices to ensure consistent accessibility across platforms. Additionally, involve people with disabilities in user testing to gain valuable feedback and insights.
Target
Target has developed an accessibility policy that includes information on how to report accessibility-related concerns, providing a clear avenue for users to address any accessibility issues they may encounter. They actively involve users with disabilities in the testing process to gather feedback and insights.
ADA Compliance Checklist for Websites
To help you ensure that your website meets ADA standards, here is a checklist to guide you through the process.
- Provide alternative text for images: Ensure that all images on your website have descriptive alternative text (alt text). Alt text allows screen readers to describe the content of an image to visually impaired users, enabling them to understand the context.
- Use proper heading structure: Organize your website’s content using appropriate heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.). Headings provide a hierarchical structure to your content, making it easier for users with assistive technologies to navigate through the page and understand its organization.
- Use descriptive link text: Avoid using vague or generic phrases like “click here” for your hyperlinks. Instead, use descriptive link text that provides information about the target page or resource. Screen readers can read the link text aloud, giving users a clear understanding of where the link will lead them.
- Ensure keyboard accessibility: Make sure that all functionality and interactive elements on your website can be accessed and operated using only a keyboard. Users with mobility impairments or those who rely on assistive devices like switches or alternative keyboards should be able to navigate your website without encountering any barriers.
- Provide captions and transcripts for multimedia: If your website includes videos or audio content, provide captions or transcripts. Captions make the audio content accessible to users with hearing impairments, while transcripts allow users to access the information in a textual format.
- Ensure color contrast: Use appropriate color contrast between the text and background throughout your website. This helps users with visual impairments, such as color blindness, to read and comprehend the content more easily. WCAG 2.1 guidelines recommend a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 for normal text and 3:1 for large text.
- Implement form accessibility: Make sure that all form fields on your website have associated labels. Labels provide context and instructions for users filling out forms, making it easier for them to understand the purpose of each field. Additionally, ensure that form validation errors are clearly indicated and communicated to users.
- Ensure resizable text: Allow users to resize the text on your website without causing any layout or functionality issues. Some users with visual impairments rely on larger text sizes to read content comfortably, and restricting their ability to resize can hinder their access to information.
- Test with assistive technologies: Use assistive technologies like screen readers, keyboard-only navigation, and voice recognition software to test the accessibility of your website. These tools can help you identify and address any accessibility barriers that may exist.
Consequences of Non-Compliance with ADA
It is crucial for businesses and organizations to understand and comply with the ADA to ensure equal access and avoid potential legal and reputational risks associated with non-compliance.
Here are some of the potential outcomes of non-compliance with the ADA:
- Legal consequences: Non-compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) can result in lawsuits and legal actions filed against the non-compliant entity.
- Fines and penalties: Violators may be subject to significant fines and penalties imposed by regulatory agencies or ordered by courts.
- Remediation costs: Non-compliant businesses or organizations may be required to make costly changes to their facilities, policies, or practices to ensure accessibility.
- Reputation damage: Non-compliance can lead to negative publicity, tarnished reputation, and loss of customer trust and loyalty.
- Limited customer base: Inaccessible premises or services can exclude individuals with disabilities, resulting in a smaller customer base and potential loss of revenue.
- Inefficient operations: Lack of accessibility may hinder the productivity and efficiency of employees with disabilities, impacting overall business performance.
- Missed business opportunities: Non-compliance may prevent partnerships, contracts, or collaborations with organizations that prioritize accessibility and inclusion.
- Discrimination claims: Non-compliance with the ADA can give rise to claims of discrimination based on disability, which can have significant legal and financial ramifications.
- Future compliance requirements: Non-compliance can trigger increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, leading to stricter oversight and compliance requirements in the future.
UserWay Offers Affordable ADA Compliance Solutions
UserWay is an accessibility technology company that aims to make websites compliant with ADA. The ADA compliant is essential for ensuring equal access to digital content for individuals with disabilities. However, many businesses and website owners struggle with the cost of implementing ADA compliance measures. Recognizing this challenge, UserWay has developed an innovative solution to make ADA compliance affordable and accessible to a wider range of organizations.
One of the key advantages of UserWay is its automated accessibility technology. The platform utilizes AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze websites and identify accessibility issues. This automated approach significantly reduces the time and effort required to manually review and fix accessibility barriers. By streamlining the process, UserWay not only saves businesses valuable resources but also makes ADA compliance more affordable.
Wrapping Up!
Implementing ADA compliance not only ensures legal compliance but also fosters a more inclusive environment, providing equal access and opportunities to people with disabilities. It is crucial for businesses to prioritize accessibility and invest in creating a barrier-free digital landscape.
Remember, ADA compliance is an ongoing process, and it requires continuous monitoring and updates. If you need further assistance or guidance, please do not hesitate to reach out to Eastmont Digital. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of ADA compliance and ensure that your digital presence is accessible to everyone. Together, let’s make the internet a more inclusive space for all individuals.





